This resource page serves as compilation of effective programming across OJJDP’s “Continuum of Care for Communities.” Additional information that is specific to serious offenses is located at the end of the document.
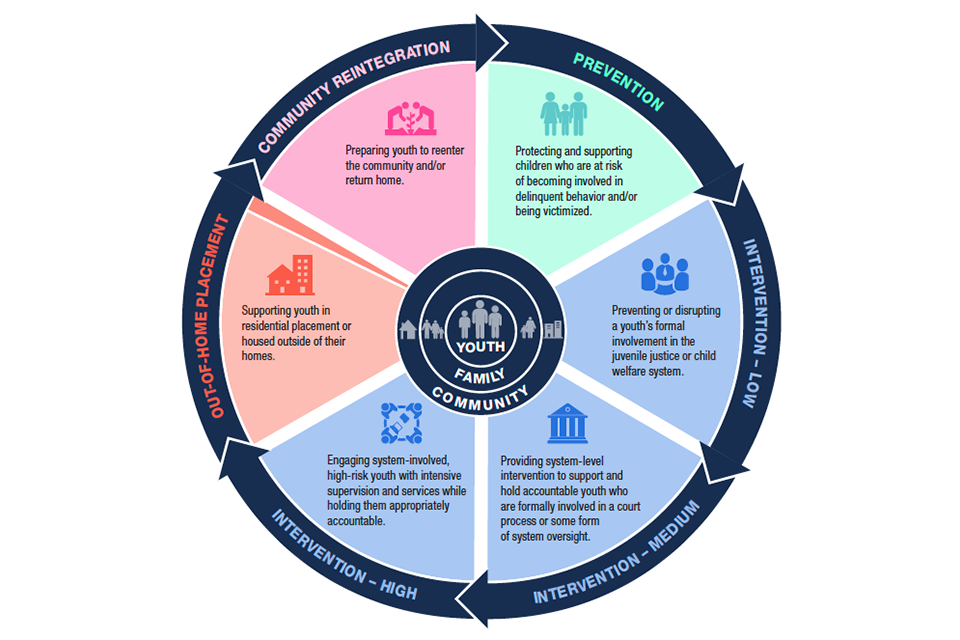
The Continuum of Care reflects a framework for youth justice services – and the dynamic and evolving nature of youth involvement in this continuum. In an effective continuum of care, the majority of youth would be served through prevention and low intervention services. The number of should decrease at each step in the continuum.
This is proven successful and cost effective. According to research from the Justice Policy Institute, the average state cost for secure confinement of a youth is $588 per day (that’s $214,620 per year), while community-based programs can cost as little as $75 per day. The Continuum of Care framework centers around the needs of youth, families and the communities.
Prevention
These efforts reduce risk factors and promote protective factors for children at risk of becoming involved in delinquent behavior or being victimized. Examples include mentoring, community violence intervention and prevention, support for children of incarcerated parents, and supporting children exposed to violence.
- Children Exposed to Violence: This literature review explores ways to help young people in the justice system that have higher than normal exposure to adverse childhood experiences, including violence (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP). Literature reviews explore both what works, and what has shown not to work.
- Child Welfare and the Juvenile Justice System: A literature review on child welfare and its intersections with the juvenile justice system (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Gang Prevention: A literature review on gang prevention and intervention programs (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Interpersonal and Conflict Resolution Skills: A literature review on ways to build and strengthen interpersonal and conflict resolution skills among youth (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Mental Health: A literature review on mental health and its intersections with the juvenile justice system (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Positive Youth Development: A literature review on ways to support positive development and build protective factors against delinquency (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Protective Factors: A literature review on protective factors that help young people avoid delinquent behavior (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- School/Classroom Environment: A literature review on the role of schools in preventing involvement with the juvenile justice system (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Status Offenses: (Truancy, Curfew Violations, Runaway, and Failure to Abide by a Parents’ Rules): A literature review that examines the common examples of non-delinquent behavior, and proven strategies to address these behaviors (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Truancy Prevention: A literature review on ways to support young people who are disengaged from school and missing excessive class time (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Youth Mentoring: A literature review on mentoring programs for youth (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
Intervention – Low
Intervention Low focuses on preventing or disrupting a youth’s formal involvement in the juvenile justice or child welfare systems, including after a youth has committed delinquent acts. Examples include pre-arrest diversion and mediation (conflict resolution that employs a neutral third party).
- After School Programs: A literature review on programs to help support young people after school hours have ended (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Diversion: An Implementation Guide for states working to create and sustain diversion programs to help young people get back on track (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Diversion: A literature review on diversion programs as alternatives to formal court processing (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Family Therapy: A literature review on how family therapy can help intervene in problematic behaviors (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Restorative Justice: A literature review on ways that restorative justice can be used to repair harm and hold young people accountable for their actions (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
Medium Intervention
These interventions support youth who are formally involved in a court process or other justice system oversight. Efforts may involve specialized services or programs targeting specific delinquent activities and/or youth. Examples include juvenile treatment and family treatment courts and restorative justice (an approach aimed at repairing the harm done to victims).
- Art-Based Interventions: A literature review on ways that arts-based programs and arts-based therapies can be used to help young people (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A literature review on how cognitive-behavioral therapy can serve as an intervention (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Drug Courts and Family Drug Courts: Literature reviews on the roles of specialty courts in addressing young people’s needs (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Gun Court: A literature review on specialty courts focused on guns (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Mental Health Courts: A literature review on specialty courts focused on addressing the needs of young people with mental illness (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Teen/Youth Court: A literature review on the teen court model (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
Intervention – High
These interventions provide intensive supervision and services that support system-involved, high-risk youth, both pre- and post-adjudication. These efforts meet the complex needs of youth on probation and under in-home monitoring by providing an array of services to help them fulfill the conditions of their adjudication. Examples include intensive wrap-around models of service.
- Alternatives to Detention and Confinement: A literature review on ways to support young people with high needs without resorting to detention or secure confinement (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Day Treatment Programs: A literature review on the use of day treatment centers as an alternative to incarceration (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Home Confinement: A literature review on home confinement as an alternative to detention (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Probation: A literature review on the way that targeted probation services can help support young people and families (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Vocational Training: A literature review on ways that job training can help young people avoid future interactions with the justice system (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
Out-of-Home Placement
Youth may be placed outside the home after the child welfare or juvenile justice systems intervene in response to the youth’s needs and risks. Examples of out-of-home placements include nonsecure placement, group homes, foster care, shelter care, and secure detention and confinement. Secure care in a locked facility should only be used for the small percentage of youth who pose a serious risk to public safety and only for limited periods of time.
- Group Homes: A literature review on ways that therapeutic group homes can help support young people and keep communities safe (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
Community Reintegration
Often called reentry or aftercare, these programs prepare youth to reenter the community and/or return home. Successful reintegration requires planning and collaboration to identify and deliver services needed by youth, families, and the community. Key components of the reintegration process include education, mental health services, housing, and family supports. Examples of programs include mentoring programs, education and employment programs, and partnerships with volunteer service organizations.
- Reentry: An Implementation Guide for states working to help young people as they return to their community (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Reentry: A literature review on reentry and ways to help ensure success for young people returning to their communities (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- ROCA: A community-based intervention program that provides intensive support and services to high-risk youth to heal trauma and learn pro-social behaviors.
- Youth Advocate Programs (YAP): A community-based program that provides continuum of care services to youth and families involved in the justice system to help heal trauma, build positive relationships and acquire new skills.
Serious Behaviors
- Community Violence Intervention: Launched in FY2022, this initiative seeks to prevent and reduce violent crime in communities by supporting comprehensive, evidence-based violence intervention and prevention programs through partnerships with community stakeholders.
- Gun Violence and Youth: A literature review on proven responses to young people who engage in gun violence (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP).
- Gun Violence (Model Programs): Includes a list of rated programs related to youth gun violence, including programs that have proven effective such as:
- Ceasefire in Oakland, Ca.: This is a focused-deterrence group violence reduction strategy (GVRS) designed to reduce or control gun violence in Oakland, Calif. (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s National Institute of Justice (NIJ).
- High Point Drug Market Intervention: A problem-oriented policing program that aims to eliminate overt drug markets and the problems associated with them through a deterrence-based, pulling-levers framework (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s National Institute of Justice (NIJ).
- Integrated Ballistics Identification Systems: This is an automated ballistics imaging and analysis system that populates a computerized database of digital ballistic images of bullets and casings from crime guns, to assist forensic experts in making identifications for police investigations and trials (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s National Institute of Justice (NIJ).
- Milwaukee Homicide Review Commission: A program that attempts to reduce homicides and non-fatal shootings through a multidisciplinary and multiagency homicide review process (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s National Institute of Justice (NIJ).
- Operation Ceasefire: This is a problem-solving police strategy, which was designed to reduce gang violence, illegal gun possession, and gun violence in communities in Boston, Mass. (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s National Institute of Justice (NIJ).
- Offender-Focused Policing: This is a proactive, hot spots policing tactic that focuses attention on people who have been convicted of violent offenses operating in neighborhoods with high violent-crime rates (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s National Institute of Justice (NIJ).
- Rockford Area Violence Elimination Network: This is a parole-based, focused deterrence intervention. The goal of the program is to reduce community-level firearm violence (from the Department of Justice (DOJ)'s National Institute of Justice (NIJ).